Why Boiler Heating Systems Are Perfect for Minnesota Homes
A boiler heating system uses hot water or steam to heat your home through radiators, baseboard heaters, or radiant floor systems. Unlike furnaces that blow heated air through ducts, boilers provide steady, comfortable warmth that doesn’t dry out your air or circulate dust and allergens.
Key Features of Boiler Heating Systems:
- Heat Distribution: Hot water or steam circulated through pipes to radiators or baseboards
- Fuel Sources: Natural gas, oil, propane, or electricity
- Efficiency: Modern condensing boilers achieve 95%+ AFUE ratings
- Comfort: Radiant heat warms objects directly for even, consistent temperatures
- Air Quality: No forced air circulation means less dust and allergens
Many Twin Cities homeowners prefer boilers because they provide more balanced heat throughout the home during harsh Minnesota winters. The radiant heat makes rooms feel warmer at lower thermostat settings compared to forced-air systems.
When Minnesota temperatures plunge, you need reliable, efficient heating that keeps your family comfortable without breaking the bank.
Boilers are the second most common heating system in North America after furnaces, but they’re gaining popularity due to their superior comfort and efficiency. Modern boiler systems are just as efficient as gas forced-air furnaces while offering quieter operation and better indoor air quality.
What is a Boiler and How Does It Work?
Instead of blowing hot air like a furnace, a boiler heating system warms your home with radiant heat, similar to how the sun warms you on a cool day. A boiler is a water heater that sends hot water (or steam in older systems) through pipes to heat your home. This method, called a hydronic system, creates a gentle, even warmth.
Unlike furnaces that push heated air through ducts, boilers radiate heat from surfaces like floors or radiators. This approach eliminates cold spots and drafts, creating a cozy environment. Because it doesn’t blow air, it also prevents dust and allergens from circulating through your home.
Modern boilers in the Twin Cities typically run on natural gas for its efficiency and convenience, though they can also use oil, propane, or electricity. Regardless of the fuel source, the principle stays the same: heat water, circulate it, and let it warm your home naturally.
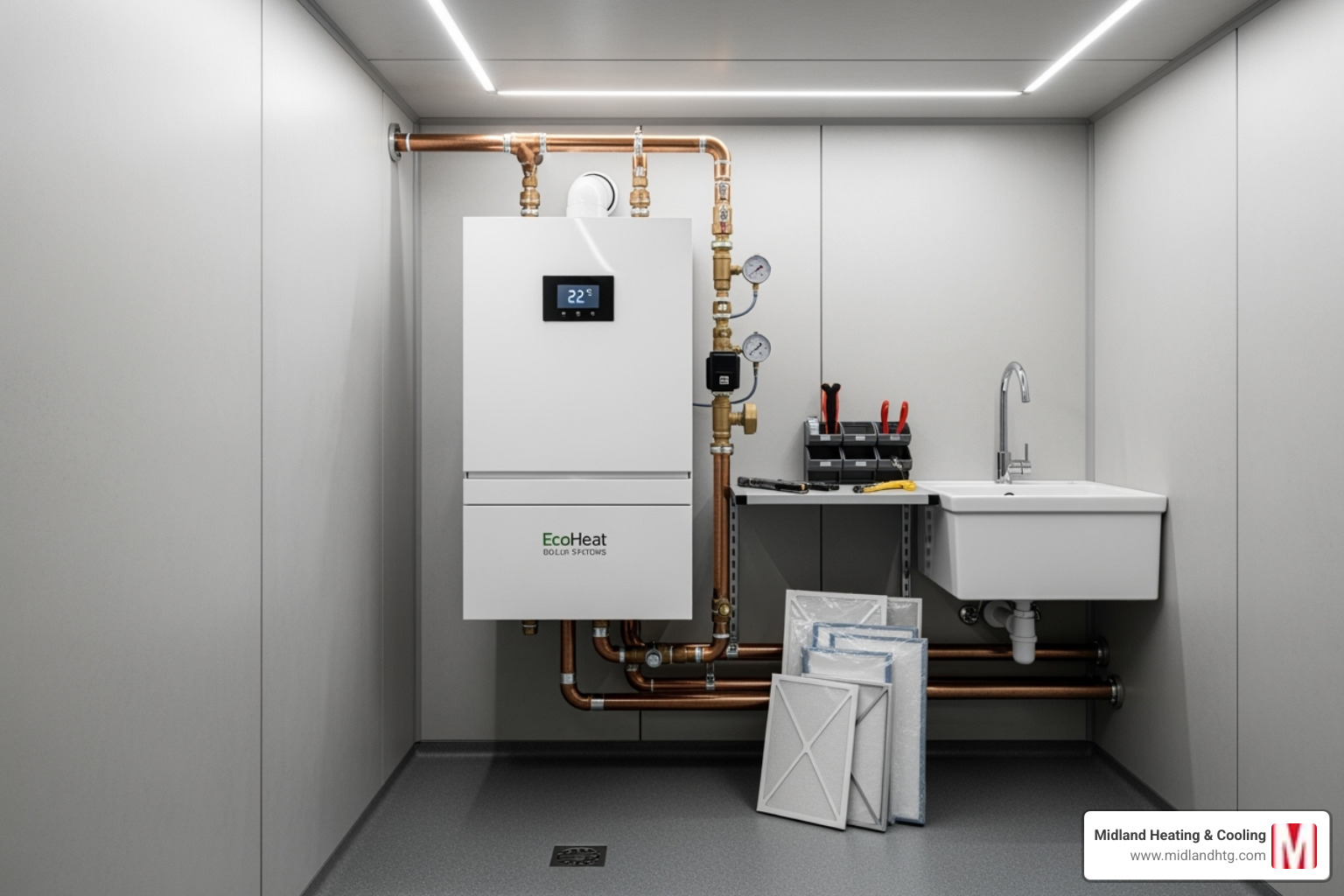
The Core Components of a Boiler System
A boiler heating system has several key components working together:
The burner creates a flame to generate heat. The heat exchanger transfers this heat to the water. The circulating pump moves the heated water through pipes. The expansion tank safely accommodates the expansion of heated water, preventing over-pressurization.
Heat emitters, such as radiators, baseboard heaters, or in-floor tubing, release the heat into your rooms. The thermostat controls the system, telling it when to turn on and off to maintain your desired temperature.
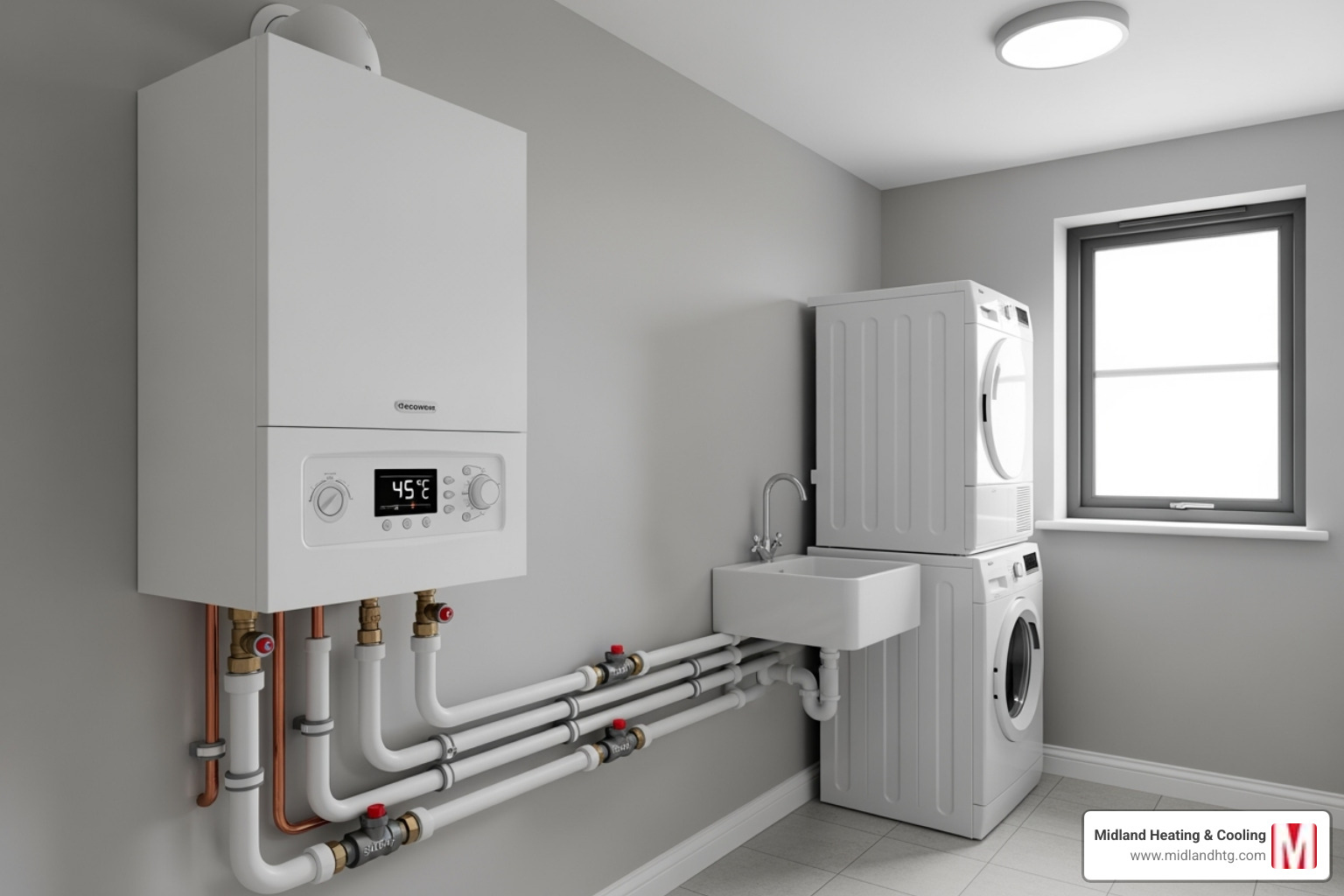
How Heat is Delivered: Hot Water vs. Steam
Boilers deliver heat using either hot water or steam.
Hot water systems are the modern standard. They heat water to 145-190 degrees Fahrenheit and use a pump to move it through a closed loop of pipes to radiators or baseboards. This closed-loop design is highly efficient, providing consistent, even heating.
Steam systems are typically found in historic homes throughout Minneapolis and St. Paul, especially those built before the 1950s. They boil water to create steam, which rises naturally through pipes to radiators. As the steam cools and condenses, it flows back to the boiler. While effective, steam systems operate at higher temperatures and require more maintenance than modern hot water systems.
Exploring the Different Types of Boiler Heating Systems
Modern boiler technology offers several options to meet different needs based on home size, hot water usage, and efficiency goals. Understanding the main types of boiler heating systems will help you choose the best fit for your Minnesota home.
Conventional, System, and Combi Boilers
The three main types of modern boiler heating systems each have their own strengths:
Conventional boilers are traditional units that work with a separate hot water storage cylinder, making them ideal for larger homes with high hot water demand.
System boilers are similar but integrate more components, like the expansion vessel and circulating pump, into the main unit for a more compact installation while still providing stored hot water.
Combi boilers are the most space-efficient option, providing both heating and hot water on demand from a single, wall-mounted unit. They are perfect for smaller homes but may have limitations if multiple hot water taps are used simultaneously.
Learn more about different boiler types.
The Benefits of High-Efficiency Condensing Boilers
High-efficiency condensing boilers are designed to extract maximum value from fuel. Unlike older boilers that vent hot exhaust gases, condensing boilers capture the latent heat from these gases by cooling them until the water vapor condenses. This recycled heat is used to help warm your home.
These units are identifiable by their PVC pipe venting, which is necessary because the condensate is slightly acidic and would corrode traditional metal flues.
The results are impressive. Modern condensing gas boilers can achieve AFUE ratings of 95% or higher, meaning 95 cents of every fuel dollar heats your home. This can lead to energy savings of 20-30% compared to older systems and reduces your home’s carbon footprint. It’s a win for your wallet and the environment.
Read about choosing the right water heating option for your lifestyle.
Boiler Efficiency, Maintenance, and Common Issues
With proper care, a boiler heating system can provide reliable comfort for 20-25 years or more. Understanding its efficiency, maintenance needs, and common issues is key to its longevity.
Understanding Boiler Efficiency (AFUE)
AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) is a percentage that measures how efficiently your boiler heating system converts fuel into heat. An 80% AFUE rating means 80 cents of every fuel dollar heats your home, while 20 cents is lost.
- Low-efficiency systems (often 20+ years old) have AFUE ratings of 56% to 70%.
- Mid-efficiency systems perform better, at 80% to 83% AFUE.
- High-efficiency systems, like modern condensing boilers, achieve an impressive 90% to 98.5% AFUE.
Upgrading from an old, inefficient boiler to a high-efficiency model can significantly cut heating bills and reduce your environmental impact.
Find out more about the standards for residential furnaces.
Essential Boiler Maintenance for Longevity
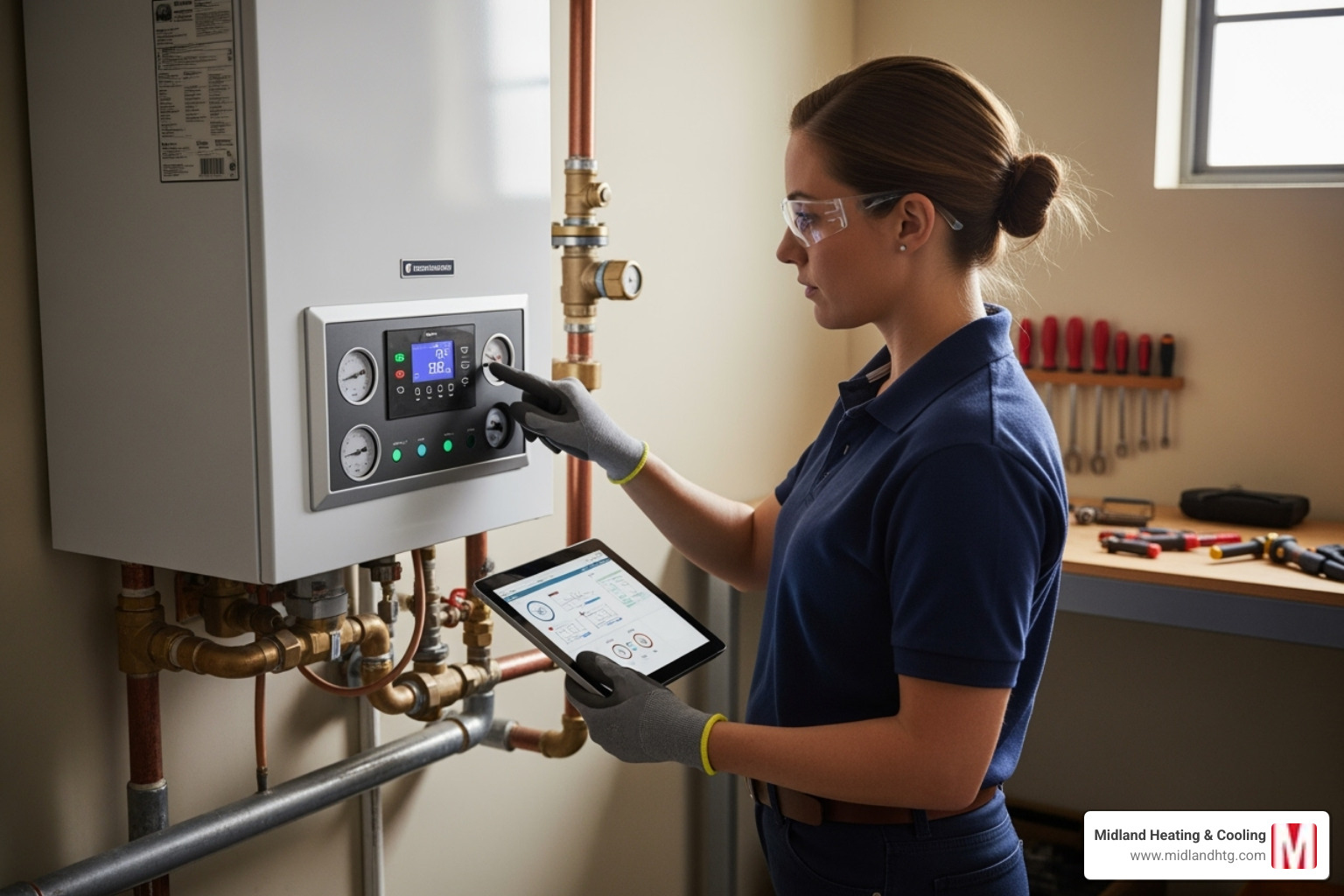
Annual professional maintenance is crucial for your boiler heating system. A certified technician will perform a combustion analysis, conduct safety checks on valves and controls, clean the burner and combustion chamber, and inspect the vent system. They will also check for fuel leaks, examine the heat exchanger, and lubricate moving parts.
Between visits, homeowners can help by checking the pressure gauge and bleeding radiators to release trapped air. If you leave for an extended period in winter, set your thermostat to at least 55°F to prevent frozen pipes. Always have working carbon monoxide detectors in your home. Proper maintenance ensures efficiency and can extend your boiler’s life to 20-25 years.
Learn more about boiler maintenance.
Common Boiler Problems and When to Call a Pro
Knowing the warning signs of boiler trouble can prevent major issues. Call a professional if you experience:
- No heat: Could be a simple thermostat issue or a major component failure.
- Low water pressure: A common reason boilers stop working.
- Leaks: Any leak from a sealed system needs immediate attention to prevent water damage and pressure loss.
- Strange noises: “Kettling” (boiling sounds) may indicate limescale buildup, while “gurgling” suggests trapped air.
- Thermostat failure: If the boiler doesn’t respond to temperature changes.
While you can check pressure or bleed radiators, most issues require a certified technician to diagnose and repair safely.
Read more about common boiler problems.
When to Repair or Replace Your Boiler
Deciding whether to repair or replace your boiler heating system is a major decision that impacts your comfort, energy bills, and budget. Sometimes a repair is sufficient, but other times, replacement is the smarter long-term investment.
At Midland Heating & Cooling, we’ve helped Twin Cities families with this dilemma since 1950. We understand that every situation is unique, and we can help you determine the best path forward.
Key Factors in the Repair vs. Replace Decision
Several factors can help you decide between repair and replacement:
- Age: Boilers typically last 20-25 years. If yours is approaching this age, replacement is often the wiser choice.
- Repair frequency and cost: If you need frequent, costly repairs, a new system may be more economical in the long run.
- Energy savings: Upgrading from an old boiler with 70% AFUE to a new 90%+ model can dramatically lower your heating bills, helping to offset the replacement cost.
- Heat exchanger condition: A failing heat exchanger is a serious safety concern and a strong indicator that the boiler has reached the end of its life.
While repairing might seem like the budget-friendly choice today, considering these factors often reveals that a new, efficient boiler offers better long-term value.
Understand when to consider a boiler replacement.
Choosing the Right New Boiler Heating System
When choosing a new boiler heating system, consider these key points:
- Proper sizing: A technician must perform a heat loss calculation to determine the right size for your home. An oversized or undersized unit will be inefficient and wear out faster.
- Fuel type: Choose the most available and cost-effective option for your area, such as natural gas, propane, or oil.
- Efficiency ratings: A high-efficiency condensing boiler with a high AFUE rating will save you money on energy bills over its lifetime.
- Features and controls: Options like outdoor reset controls can improve comfort and efficiency.
- Warranty: Compare warranty terms from reputable manufacturers for peace of mind.
- Professional installation: Expert installation is critical for safety, performance, and longevity. A certified technician will ensure proper venting and integration with your existing system.
Choosing a new boiler is an investment in your family’s comfort. We’re here to make sure it’s the right choice for your needs.
Find out what to expect during boiler installation.
Frequently Asked Questions about Boiler Heating Systems
We get many questions from homeowners throughout the Twin Cities area about boiler heating systems. Here are answers to the most common ones:
Are boiler heating systems better than furnaces?
The choice between a boiler and a furnace depends on your priorities.
- Comfort: Boilers provide radiant heat, which creates an even, consistent warmth without the drafts or stuffiness of forced-air systems.
- Indoor air quality: Because they don’t use ducts to blow air, boilers don’t circulate dust, pollen, and other allergens, which is a major benefit for those with allergies or asthma.
- Noise levels: Boilers operate almost silently.
- System suitability: A furnace may be more practical if your home already has ductwork for central air conditioning. If you have or want radiators, baseboards, or in-floor heating, a boiler is the ideal choice.
How much does a new boiler system cost?
The cost of a new boiler heating system depends on several factors:
- Boiler type and size: A combi boiler for a small home will cost less than a conventional system for a large one. The unit must be correctly sized for your home’s heating needs.
- Efficiency rating: High-efficiency models have a higher upfront cost but provide long-term savings on energy bills.
- Installation complexity: Replacing a similar unit is less expensive than installing a new system with all-new piping and heat emitters.
We provide detailed estimates based on a thorough assessment of your home.
Can I switch from a furnace to a boiler?
Yes, you can switch from a furnace to a boiler, but it is a significant project. Since furnaces use ductwork and boilers use pipes, the conversion requires installing a completely new distribution system. This involves removing the furnace, running a network of pipes throughout the home, and installing heat emitters like radiators or baseboard heaters in each room.
Due to the labor and materials involved, this is a major renovation. However, many homeowners find the superior comfort and air quality of a boiler heating system to be a worthwhile investment. A professional consultation is the best first step to assess your home’s layout and discuss all options.
Conclusion
A boiler heating system is an excellent choice for Minnesota homes, offering superior comfort, quiet operation, and better indoor air quality. The radiant warmth boilers provide creates a cozy, even heat without circulating dust and allergens.
Whether you are choosing a new high-efficiency model or maintaining your current one, a well-cared-for boiler is a smart, long-term investment that can provide reliable heating for 20-25 years or more.
At Midland Heating & Cooling, we’ve specialized in boiler systems for Twin Cities families since 1950. Our certified technicians have the expertise to handle everything from installation to maintenance and repairs, ensuring your home stays comfortable all winter.
Don’t let heating worries keep you up at night! For expert service and support with your boiler, from routine maintenance to emergency repairs, contact our certified technicians today. We’re here to ensure your home stays perfectly warm and comfortable, all winter long.