Don’t Let Your Home Turn into an Igloo
Waking up to a cold house on a chilly Minnesota morning is the worst feeling. You’re bundled in thick socks, a scarf, and still shivering. Your furnace not heating can quickly turn your cozy home into an icebox. It’s a common problem, and often, the fix is simpler than you think. Before you panic and call for an emergency repair, there are a few quick checks you can do yourself.
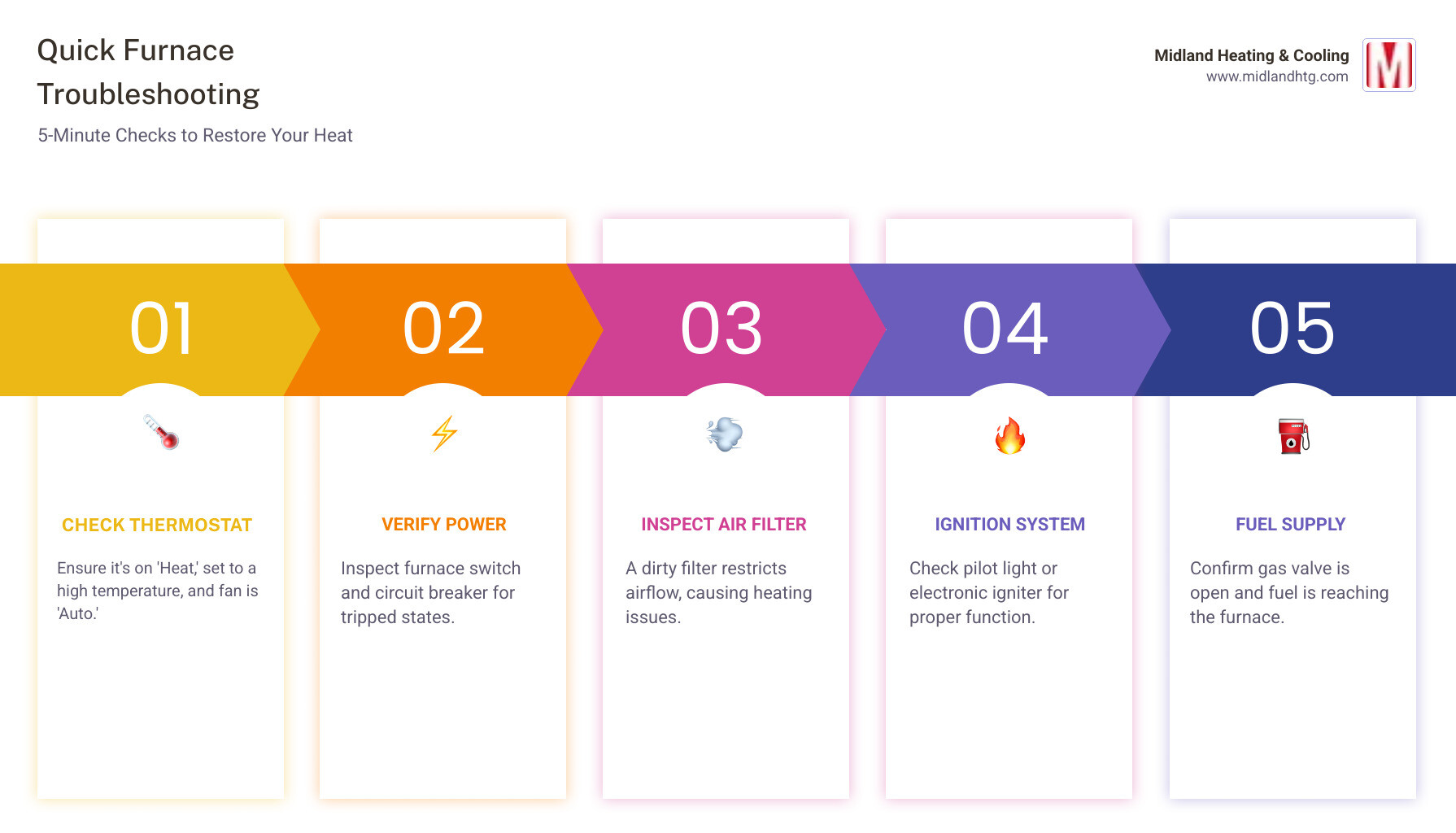
Here’s a rapid-fire troubleshooting guide to get you started:
- Thermostat Settings: Is it on “Heat”? Is the temperature set high enough? Is the fan on “Auto”?
- Power Supply: Check your furnace switch and the circuit breaker.
- Air Filter: A dirty filter can block airflow and cause issues.
- Pilot Light/Ignition: Is the pilot light out, or is the electronic igniter working?
- Gas Valve: Make sure the gas valve is open and supplying fuel.
Many times, these simple steps can restore warmth to your home in minutes.
Start Here: 5-Minute Fixes for a Furnace Not Heating
Before you assume the worst, let’s cover the simple checks that often solve the problem. These quick steps can save you from an unnecessary service call.
Check Your Thermostat Settings
Your thermostat controls your furnace, and incorrect settings are a common cause of a furnace not heating.
- Mode: Ensure it’s set to “Heat,” not “Cool” or “Off.”
- Temperature: Set the temperature at least five degrees higher than the current room temperature to trigger a heating cycle.
- Fan: The fan should be on “AUTO,” not “ON.” The “ON” setting blows air continuously, even when it’s not being heated.
- Power: For digital models, check the batteries. A blank or flickering screen often means they need replacing. If you have a smart thermostat, a simple reboot can sometimes resolve connection glitches.
Verify Power to the Furnace
A furnace can’t run without electricity. This basic check is a critical step.
- Find the furnace power switch, which looks like a light switch on or near the unit, and make sure it’s on.
- Check your home’s electrical panel for the breaker labeled “Furnace” or “HVAC.” If it’s tripped (in the middle position), flip it off and then back on to reset it.
- Ensure the furnace panel door is securely closed. A safety switch prevents the furnace from running if the panel covering the blower is ajar.
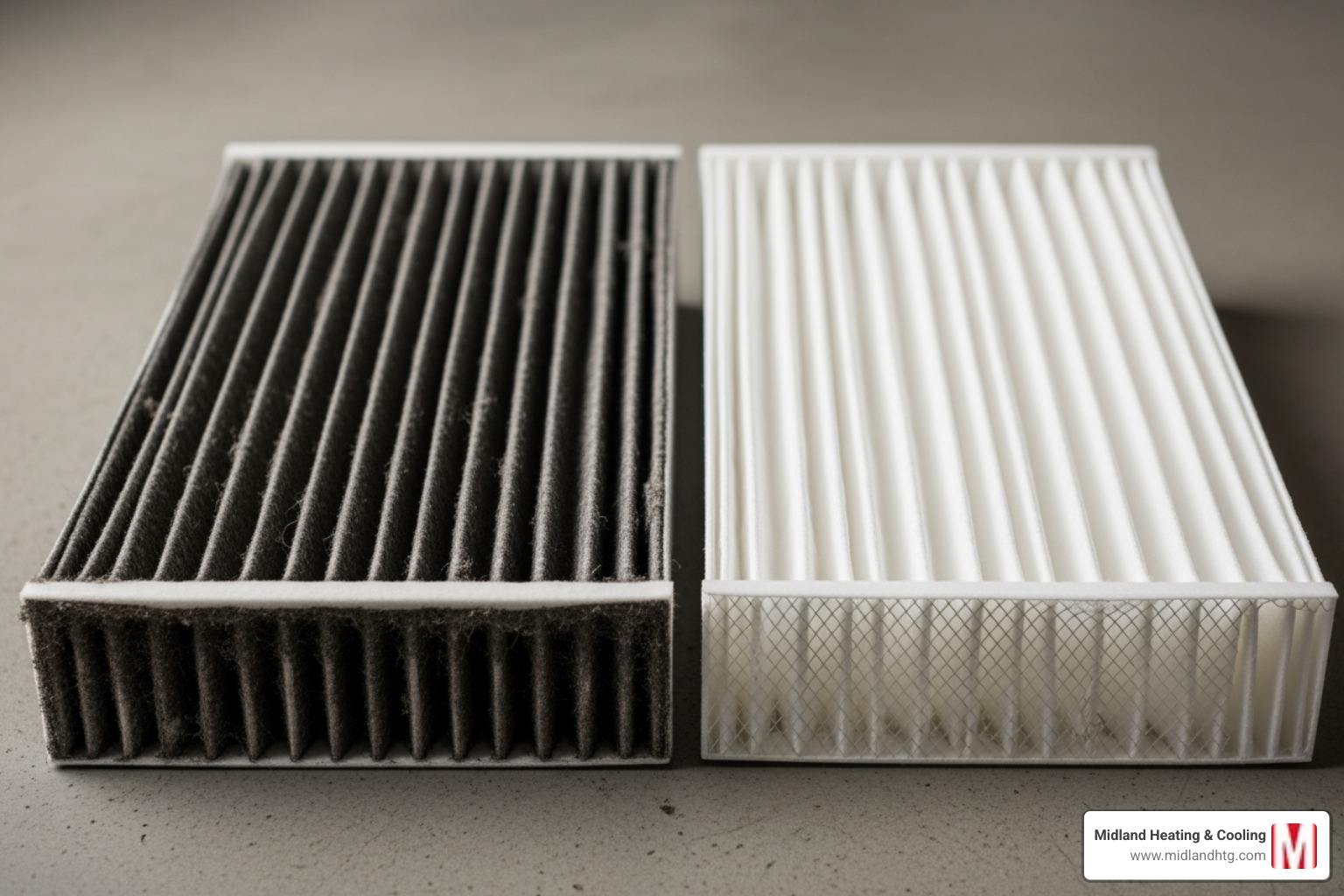
Inspect the Air Filter
A clogged air filter is one of the most common reasons a furnace not heating issue occurs. It restricts airflow, forcing your furnace to work harder and potentially overheat. When the furnace gets too hot, a high-limit safety switch will shut it down to prevent damage.
Check your filter monthly during heating season. If you can’t see light through it, it’s time for a change. As a general rule, replace filters every 1-3 months, depending on the filter type and factors like pets or allergies in the home. Regular filter changes not only prevent heating issues but also improve air quality and More info on improving efficiency.
Intermediate Troubleshooting: Common Component Failures
If the quick fixes didn’t work, the issue might lie with a specific component. These steps are more involved but can often be handled by a confident homeowner.
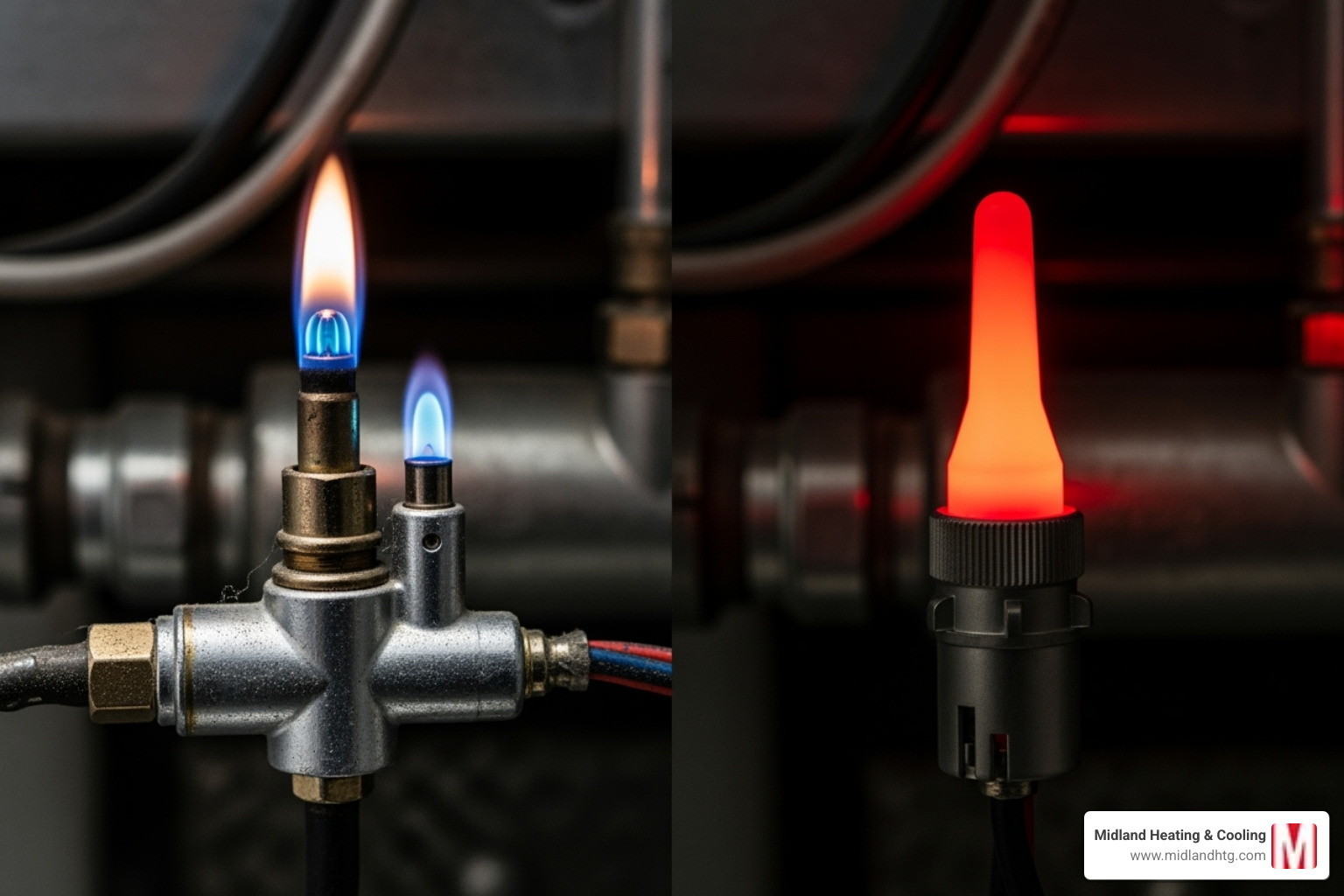
Issues with the Pilot Light or Electronic Ignition
Your furnace’s ignition system is what starts the heating process. Older furnaces use pilot lights, while newer ones use electronic ignition.
- For Furnaces with a Pilot Light: This is a small, continuous flame that ignites the main burner. If it’s out, you can usually relight it by following the instructions on a label inside the furnace. If the pilot light won’t stay lit, it could be due to a dirty thermocouple, which is a safety device that senses the flame.
- For Furnaces with Electronic Ignition: These systems use an igniter only when heat is needed. You might hear a clicking sound or see a brief glow as it tries to start. If it fails, the igniter may be dirty or faulty. Many modern furnaces also have blinking LED lights on the control board that display error codes to help diagnose the problem.
| Feature | Older Furnace (Pilot Light) | Newer Furnace (Electronic Ignition) |
|---|---|---|
| Ignition Type | Standing pilot light (always on) | Intermittent pilot or hot surface igniter (activates on demand) |
| Troubleshooting | Check if pilot light is out, relight following manual. | Listen for clicking/see glow; check for error codes; igniter may be dirty/faulty. |
| Common Fixes | Relight pilot, clean/replace thermocouple. | Clean igniter, replace igniter, replace ignition control module. |
| Safety Concerns | Pilot light can go out, gas can accumulate if not sensed. | Malfunctioning igniter can prevent safe ignition. |
Problems with the Fuel Supply
No fuel means no heat. If your furnace not heating is the problem, check your fuel source.
- Natural Gas: Ensure the gas valve on the supply line to your furnace is “on” (handle parallel to the pipe). Also, check with your utility provider for any local service interruptions.
- Propane or Oil: Check the gauge on your tank to make sure it’s not empty. For oil furnaces, a clogged oil filter can also block fuel from reaching the burner.
How to Address a Dirty or Faulty Flame Sensor
A flame sensor is a safety device that confirms a flame is present. If it’s dirty, it can’t detect the flame and will shut the furnace down after a few seconds. This “short cycling” is a classic sign of a dirty flame sensor.
You can often clean the sensor yourself:
- Turn off all power to the furnace at the switch and breaker.
- Locate the flame sensor, a thin metal rod near the burners, and carefully remove it.
- Gently clean the rod with fine-grit sandpaper or steel wool to remove carbon buildup.
- Reinstall the sensor, restore power, and test the furnace.
If cleaning doesn’t solve the short cycling, the sensor may be faulty and need professional replacement.
Deeper System Problems & When to Be Cautious
If you’re still without heat, the problem may be more complex. These issues often involve safety systems designed to protect your furnace. We recommend professional assistance for these problems to ensure your safety and prevent further damage.
Signs Your Furnace is Overheating
A furnace can overheat, usually due to restricted airflow. To prevent damage, a high-limit switch will shut down the burners, though the fan may continue to run to cool the unit down. This is why you might feel cold air blowing from your vents.
Common causes of overheating include:
- A severely clogged air filter.
- Blocked return air vents.
- Too many closed supply vents throughout the house.
- A malfunctioning blower motor.
If your furnace repeatedly starts and then shuts down, it’s likely overheating. While checking your filter and vents is a good first step, persistent overheating requires a professional to diagnose and prevent damage to the heat exchanger.
Blocked Vents and Ductwork Issues
Even if your furnace is producing heat, it won’t warm your home if the air can’t circulate properly. A furnace not heating your living space could be a distribution problem.
- Check Vents and Registers: Walk through your home and ensure all supply registers are open and not blocked by furniture or rugs.
- Leaky Ductwork: Cracks or loose connections in your ductwork can let heated air escape into your attic or basement. This leads to higher energy bills and cold spots in your home. Sealing accessible leaks with metal duct tape can help, but significant ductwork issues require professional repair.
Potential Problems with the Furnace Control Board
The control board is the “brain” of a modern furnace. If it malfunctions, your furnace may not work at all, or it might behave erratically.
Symptoms of a failing control board include:
- The furnace doesn’t respond to the thermostat.
- The blower fan runs constantly or not at all.
- The furnace shuts down unpredictably.
- Blinking LED lights on the control board itself, which are diagnostic codes that can tell a technician what’s wrong.
Replacing a control board is a job for a qualified HVAC technician. If you suspect a control board issue, note any blinking light patterns and call for professional help. For more information, see our guide on Signs You Need Furnace Repair.
Safety First: Critical Furnace Warning Signs
Some furnace problems are more than an inconvenience—they’re a safety risk. If you encounter any of the following warning signs, stop troubleshooting and call for emergency help immediately.
What to Do if You Smell Gas
Natural gas has a distinct rotten egg smell added to it for safety. If you smell this in your home, you may have a dangerous gas leak.
Follow these steps immediately:
- Do not use any electronics, flip light switches, or use your phone inside the house. A single spark could be catastrophic.
- Evacuate everyone from the home immediately.
- Once you are safely outside and away from the house, call 911 and then your gas utility company.
- Do not re-enter your home until emergency services have declared it safe.
Carbon Monoxide Risks and Prevention
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless gas produced by the incomplete combustion of fuel. It is extremely dangerous and can be fatal.
- Install CO Detectors: Place carbon monoxide detectors on every level of your home, especially near sleeping areas. Test them monthly and replace batteries annually. If an alarm sounds, evacuate immediately and call 911.
- Check the Burner Flame: A healthy furnace flame is steady and blue. If you see a yellow, orange, or flickering flame, it’s a sign of a combustion problem that could be producing CO. Shut off the furnace and call a professional.
- Cracked Heat Exchanger: This is a serious hazard that allows CO to mix with your home’s air. A cracked heat exchanger is not visible to the naked eye and requires a professional inspection to detect.
Regular maintenance is the best way to prevent these dangers. When safety is a concern, Professional Heater Repair is Essential.
When to Stop and Call a Professional
Knowing your limits is key to safe and effective DIY. For complex or unsafe situations, calling a professional is the smartest move to avoid bigger problems or safety hazards.
You’ve Tried Everything and Still Have a Furnace Not Heating
You’ve checked the thermostat, power, filter, and ignition system, but your furnace not heating problem persists. If you’ve exhausted the basic troubleshooting steps, or if the problem is intermittent and hard to pin down, it’s time to call an expert. If at any point you feel uncomfortable or unsafe, stop and make the call.
You Hear Loud or Unusual Noises
Your furnace should operate with a gentle hum or whoosh. Loud, sudden, or strange noises are a cry for help and signal a mechanical problem.
- Rattling: Could be a loose panel or debris in the system.
- Squealing: Often points to a problem with the blower motor belt or bearings.
- Banging or Clanking: May indicate a serious issue with the blower assembly or ductwork.
- Grinding: This is a critical warning, usually signaling failing motor bearings that could lead to a total breakdown.
Turn off the furnace and call a technician to diagnose these sounds, as they often point to parts that are about to fail.
Your Furnace is Over 15 Years Old
Most furnaces have a lifespan of 15 to 20 years. As they age, they become less reliable and efficient. If your older furnace is causing problems, consider whether a repair is worth the cost.
Signs it might be time to replace your furnace include:
- Rising Energy Bills: A sign of declining efficiency.
- Frequent Repairs: If repair costs are adding up, a new unit may be more economical.
- Uneven Heating: An aging furnace may struggle to distribute heat evenly.
A professional can give you an honest assessment of your old furnace and help you decide between repair and replacement. Our Expert Heater Repair Services include these evaluations. You can also find a certified technician for guidance or read our guide on When to Consider Furnace Replacement.
Frequently Asked Questions About Furnace Heating Issues
Over our decades of service, we’ve answered countless questions about furnace problems. Here are some of the most common ones.
How often should I change my furnace filter?
There’s no single answer, but here are some solid guidelines.
- General Rule: Check your filter monthly and replace it when it’s dirty. For most homes, this is every 1-3 months.
- Filter Type: Basic fiberglass filters may need monthly changes, while high-efficiency pleated filters can last longer.
- Home Environment: If you have pets or family members with allergies, plan to change the filter more frequently, likely every 30-60 days.
Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendation on the filter packaging. A clean filter is the easiest way to prevent a furnace not heating.
What’s the difference between troubleshooting an old vs. a new furnace?
Troubleshooting varies greatly by furnace age.
- Older Furnaces (pre-1990s) are more mechanical. They often have standing pilot lights that you can see and may need to relight. Their components are generally simpler to identify.
- Newer Furnaces are electronic and complex. They use electronic igniters and are run by a control board. Instead of a pilot light, they often have diagnostic LED lights that flash error codes to identify specific problems. They also have more safety sensors that can shut the system down.
How does regular maintenance prevent my furnace from not heating?
Annual professional maintenance is the best way to ensure reliability and prevent a furnace not heating emergency. During a tune-up, a technician will:
- Clean and inspect key components like burners, sensors, and the blower motor.
- Lubricate moving parts to reduce wear and tear.
- Perform safety checks for gas leaks and carbon monoxide risks.
- Make efficiency adjustments to save you money on utility bills.
Regular maintenance extends your furnace’s lifespan, improves efficiency, and catches small problems before they become expensive breakdowns. Learn more with our Effective Furnace Maintenance Tips.
Get Your Heat Back On with Expert Help
We hope this guide has empowered you to tackle common furnace issues. Understanding your system is the first step to staying warm.
However, some problems require a professional touch. If you’ve tried these fixes and your furnace not heating problem continues, or if you’ve encountered any safety warnings like the smell of gas, it’s time to call for help. Your family’s safety and comfort are what matter most.
At Midland Heating & Cooling, we’ve been serving the Twin Cities, Minnesota area since 1950. We are committed to 100% customer satisfaction with certified technicians who provide flexible, on-time service. We’ve built our reputation on providing reliable customer care to keep our neighbors warm through every Minnesota winter.
Don’t shiver in the cold. Whether you need an urgent repair or want to schedule proactive maintenance, our team is ready to bring the warmth back to your home.
Contact us for expert HVAC service in Minneapolis and let us help.